|
 |
- Search
| Chronobiol Med > Volume 5(4); 2023 > Article |
|
Abstract
This study is a review of articles from 1999 to 2023 that present how circadian rhythm and factors have created an impact on individuals. Chrononutrition is the latest concept of sleeping patterns and eating behaviors along with it. It includes meal frequency, regularity, and timing. Alteration in these can be a reason for healthy eating or risk of diseases. The pros and cons of chronotypes (morning and evening) and their relation with modernization are being studied. Meal skipping and its influence on body weight are deleterious for health and breakfast skipping and late dinners have a higher association with weight gain. Disruption in sleep and high-calorie consumption before bedtime causes disturbed and insufficient sleep. Nutrient intake is low in individuals who have poor sleep-wake cycles. Also, irregularity in the sleep-wake cycles and meal timings have an association with poor academic performance of students of school, college, and university levels. In conclusion, eating with a biological clock can help individuals reverse or recover from a disease and create a positive impact on academic performance.
Chrononutrition (chrono=related to time) means interaction between eating patterns throughout the day and their metabolic effect on human health. Meal timing, frequency, and regularity of food intake interact with biological rhythms throughout the day. Several factors influence both the eating habits and biological rhythms that can increase the chances of metabolic diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, obesity, depression, etc. [1]. Biological rhythms are also known as circadian rhythms (circa=about, dian=day). It involves metabolic, behavioral, and physiological cycle that is essential for daily life. It is controlled by various molecular oscillators known as “clock genes” in the suprachiasmatic nuclei of the hypothalamus and in metabolically active tissue and organs [2]. This cycle has a length of 24 hours which is genetically determined and regulated via daylight [3,4]. Molecular mechanism is a transcriptional-translational feedback loop, which is autoregulated. This means that transcription of clock genes is regulated by their protein products [5,6]. Due to modernization, increased work hours and exposure to artificial lights have disturbed the circadian system because light is the major cue for synchrony. Disturbances in the sleep/wake pattern can impact glucocorticoids and melatonin, leading to conditions such as depression, mood disorders, insomnia, and generalized anxiety [7]. Circadian rhythm and food intake behavior are recognized and hold importance. Energy intake and distribution throughout the day is not entirely known and multiple issues related to it [8]. Moreover, taking 4–5 meals in a day that are nutrient-rich is better than 3 major meals. In this way, a person will achieve their daily need for different food groups [4]. Food and nutrition synchronize circadian clocks. Different foods, time, and frequency of consumption optimize body block and explain eating habits of a person [9]. Energy expenditure, body temperature, and metabolism levels exhibit diurnal variations. Metabolism is affected by the circadian oscillators present in hormonal tissues [10,11]. Research has shown that sleep cycle and meal patterns have been changing with the change in society (modernization). This contributes to changing eating behavior and many physiological factors are affected by it [12]. Disturbance in sleep patterns causes hormonal imbalance which leads to insulin insufficiency, obesity, and eventually diabetes [13]. In adults, academic activities/social work forces them to work late hours at night which leads to breakfast skipping in the morning and an increase in evening food consumption [14,15]. Studies have shown that students with late chronotype are associated with poor mental health, physical health and affect their academic performance by fatigue, tiredness, and illness [16]. Chrononutrition could be the tool for weight management and correct eating behaviors. Insulin resistance and glucose tolerance could be improved by optimizing eating patterns and preventing future risks of diabetes [17,18]. Therefore, dietary restriction improves overall health and enhances life quality with longevity [19,20]. Managing feeding and fasting cycles can prevent chronic diseases and reverse them [21]. Circadian rhythm dysregulation can cause gastrointestinal issues or worsen symptoms of current issues since the dysregulation causes a change in eating behavior [22]. Therefore, timed meals play an important role in synchronized peripheral circadian rhythm and are effective for nearly every individual [23].
Chrononutrition is the study of the interaction between nutrition and biological rhythms that affect the health of an individual. It presents the energy distribution in humans, along with frequency, regularity, and duration of meal consumption period [24]. Chrononutrition or the food intake according to circadian rhythm is currently a topic of study since it has a relation with health [25]. This discussion first came into being in 1999 when the influence of meal timing and energy distribution was first discussed. The circadian rhythm is a natural process of regulating the sleep and wake cycle every 24 hours. The daily biological rhythms, synchronizing physiology, and behavior are supervised by the circadian timing system. Nutrition intake plays a major role in the regulation of circadian rhythmicity. Chrononutrition not only takes account into healthy well-being but also helps in improving metabolic and chronic diseases [1,26]. The interaction between eating patterns and the sleep-wake cycle shows how healthy a lifestyle one has [27]. Moreover, treating diseases through this approach has been in consideration for a long time now. Metabolic diseases are more than common in almost every population. Obesity and diabetes mellitus type 2 (DMT2) are leading health concerns around the globe [28,29]. This dietary intervention has been used to treat many diseases. Obesity and DMT2 are of them [23]. Risk of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) can be controlled by managing the biological clock and food intake as per the researchers’ conclusion [30]. A study was conducted on mice and then applied to humans. The results showed improved cardiometabolic biomarkers which were related to reduced risk of obesity and DMT2. The improved dietary pattern with circadian rhythm has been helpful [31]. To improve health, one has to reduce the eating window. A reduction in the eating window from 12–14 hours to 8–10 hours. has shown potential health benefits in individuals with obesity and any metabolic disease.
Time-restricted feeding (TRF) focuses on the time window that is best for food intake. TRF promotes the regulation of the circadian rhythm of food intake which protects against many metabolic disorders that are caused by unbalanced and adverse nutrient intake [32]. The coordination between the circadian clock and nutrient sensing pathways regulates metabolic health by feeding and fasting cycle [33]. A study suggests that implementing TRF by providing food every 3 hours within a 12-hour eating window is significantly more beneficial than allowing free access to food over the same 12-hour period [34]. Eating at an inappropriate time can disturb the body’s hormones and can cause a visible imbalance in them. A systemic review of five general databases and six nutrition journals was assessed to detect all the studies published between 2014 to 2016 to evaluate the effects of TRF on the human population. Their objective was to identify if TRF could become a dietary approach to improve health concerns. TRF differs from other dietary interventions and produces beneficial effects on health markers. This suggests that not only the quantity and quality of food but also the timing of food intake affects metabolic health. Also, this approach has been beneficial in animal models, especially rodents [35]. It shows that meal timing and amount both are linked to one another, thereby providing advantageous effects on the gut and overall health.
The circadian rhythm of young adults is disturbed since they have an irregular eating pattern and timing which affects their overall health. Currently, it bringing in major health issues since students do not follow a routine or stay on track to maintain a diet around the clock. The energy distribution in food is not calculated properly. Therefore, they face diseases that alter their daily routine tasks. Also, it disturbs their weight, academic performance, and further capacity to maintain healthy eating habits. Disturbed eating cycles can negatively influence health which causes weight gain or loss without trying. Previously, there was no authentic tool that was developed to directly assess meal intake concerning time. The questionnaire was first developed in 2020 and research is being conducted to check its validation and reliability. Eating pattern affects an individual’s weight which further determines the risk of other complications associated with it. In a study of the general population, researchers linked circadian rhythm with body weight and energy balance and concluded that circadian misalignment is a risk factor for obesity. Shift workers and those with jet lag result in later meal pattern consumption which is unfavorable times of energy and macronutrient metabolism [36,37]. Timing of any meal of the day greatly influences the risk of obesity and metabolism. In a review of multiple studies, the timing of food intake is an external synchronizer and plays an important role in obesity and weight loss programs.
Sleep has a profound effect on the body weight. Insufficient sleep and circadian rhythm misalignment are very common. Insufficient sleep is defined as sleep less than 5–6 hours per day. It can also be due to an imbalance in hormones that play a role in hunger and satiety hormone levels. People of different chronotypes (morning and evening) have different body types. These can either be inherited or due to irregular eating patterns for a long time. The sex of an individual also holds importance in determining an individual’s chronotype. Prevalence of evening chronotype is more common in men rather than in women. On the other hand, women who have children have morning chronotypes [38]. An individual skipping breakfast leads to obesity and delayed consumption of lunch hinders weight loss mostly in the ones with genetic variation in perilipin. Also, it has a deleterious effect on the diversity and composition of the gut. Also, the risk of obesity increases five times in individuals who consume food 2 hours before bedtime (evening chronotype) [39]. Another research concluded that sleep deprivation, artificial lightening, and work during night hours play a crucial role in obesity development. Also, the relation between circadian rhythm and gut microbiome, and endocrine chemicals lead to weight gain and metabolic disorders that are associated with it [40]. The research was conducted on mice to prove that desynchrony in circadian rhythm promotes weight gain and alters glucose homeostasis. They used mice with genetically ablated clock functions under different light and feeding conditions and studied their glucose and metabolic homeostasis. This discloses the importance of synchronized eating with the clock to maintain metabolic homeostasis [41].
Obesity is a growing problem and is considered an increasing global pandemic and a consequence of the imbalance between energy consumption and utilization [42]. Experts predicted that the prevalence of individuals with obesity will be 50% by 2030 [43]. In 2021, researchers from Italy conducted a study on energy balance and control of body weight. Body weight is maintained if there is a dynamic process in which energy consumption is equal to energy expenditure. If the balance is disturbed due to meal timing and circadian rhythm, it leads to weight gain. This study concluded that higher calorie food consumption in the morning reduces the susceptibility to weight gain than food consumption in the later evening. The alignment and balance between meals and sleep timing can become an important factor in controlling weight gain. Moreover, this strategy can be used with any dietary intervention which would assure weight loss and reduce positive energy balance [44]. A study showed that individuals who took a high-fat diet 1.1 hours before melatonin onset had more body fat than the ones who were lean [40]. It alters a person’s mind, influences body weight, and alertness, and hinders daily activities due to disturbed routines. Furthermore, insufficient sleep is associated with a 38% increase in obesity as compared with regular sleep [42]. They can be due to modern work patterns, disturbing substances, screen time, and stress. These all are eventually metabolic stressors. These stressors are around everyone now hence students are highly attracted to and affected by them. Research published in 2022 indicates that insufficient sleep leads to the burning of approximately 100 kcal/day, while also showing an increase of around 250 kcal/day [42]. Therefore, circadian misalignment increases the risk of obesity since it reduces energy expenditure in 24 hours. Weight loss can be vigorous if the TRF approach is used.
In a study of 2021, a chrononutrition weight reduction program recruited 91 obese individuals who were non-shift workers, which carried for 12 weeks. They were provided with proper and counted energy, protein, and fat intake. The weight loss outcome was satisfactory since it was 3% of the total body weight [45]. Therefore, improving weight loss through managing food intake with your biological clock tends to have a higher influence on an individual than eating without restricting any part of the day. Chrononutrition is of help in these scenarios. Over the past years, the urban population has increased. The majority of families have turned their way to urbanization due to the facilities they get. But with facilities and luxuries, many disturbances come together and alter the way of living [46]. There is an indisputable link between circadian rhythm and human health. A nutritional regime that follows our biological clock influences metabolism and nutrient consumption. The timing, frequency, and regularity are the main components of chrononutrition. An irregular sleep pattern leads to irregular meal consumption. Later time meal consumption can cause adiposity, DMT2, and CVDs [3].
In urban regions, people have chosen calorie-dense food mostly in the evening times either to fill hunger or cravings. This has become a cause of many diseases. In a study, women were associated with poor sleep due to food choices like fast food consumption and food higher in fats [46]. Therefore, energy intake along with dietary composition prevents circadian desynchrony and helps improve metabolic risks [47]. An individual’s metabolism is affected by the nutritional composition of any food they eat. Eating calorie-dense food in the morning is considered healthier since it provides energy for everyday activity. When an individual opts big meal at night, the body does not metabolize it completely since there would be no activity later. Not only does it influence your sleep and body shape but your gut microbiota is disturbed. Also, your mind does not work properly the next day due to poor sleep. Studies have proven that glucose tolerance is higher in the morning and exhibits better insulin secretion than at night. Therefore, the meal consumed at night impairs glucose tolerance and makes an individual insulin-sensitive. Another study observed that insulin sensitivity was impaired by 34% in the evening as compared to the morning after an intravenous glucose tolerance test was done in normal-weight participants [48].
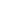
Frequency and regularity in these patterns can cause permanent damage to many of the above areas. Weight reduction programs have improved the lifestyle of many people including proper meals with nutrients, meal timing, night eating syndrome scores, and sleep patterns. They have reported feeling much better after waking up. Therefore, chrononutrition is shaping people’s life styles and quality of life [18]. In Pakistan, currently no evidence explains how the poor lifestyle of students is modifying their way of living. They are living by consuming an unbalanced diet and without any particular time of the day. According to World Health Organization, Pakistan is at the top of the list of diabetes. This can be corrected by using the TRF approach before they are diagnosed diabetic with proper tools, monitoring their diet, and recommending physical activity. Current studies suggest that timing of meals, frequency of meals, skipping meals, and fasting are linked to metabolic syndrome. Eating regularly and in the morning has a protective effect on metabolic syndrome whereas skipping breakfast and eating one meal per day harms adults causing them to be at a risk of metabolic syndrome [49]. A prospective study has suggested high disease risk in individuals who consume >6 meals per day. Other than this, it is important to consider breakfast eating, distribution of total calories per day, and night-time eating. Also fasting period between the meals is an important factor to note. Alteration in meal frequency and timings exerts positive or negative effects on individuals. Breakfast intake, the meal consumed majorly in the daytime, and less meal frequency have shown improved physiological benefits and are vital for optimal health [50]. A study has shown the effects of breakfast skipping, late lunch, and late dinner. They concluded that breakfast at 09:00 h is beneficial for health. The ones, who skip it, face difficulty in compensating their calories in the day. Also, they have a higher intake of fat and energy whereas they have a low intake of foods that contain vitamins and minerals. Lunches in the later afternoon, after 15:00 h, hinders weight loss and leads to overweight/obesity [51]. Dinner consumed before 21:00 h is advantageous for health since glucose tolerance is higher. Hence if these patterns are being followed by individuals, they are definitely in a safe zone (Figure 1) [39].
A study done on middle-aged to older age adults suggested that individuals who had a majority number of meals in the morning after waking up and fewer meals close to bedtime had lower body mass index (BMI) but different chronotypes had different results. Furthermore, the consumption of time of carbohydrate and protein-rich meals is directly associated with obesity [52]. Also, eating or drinking long before bedtime reduces the chances of long or short sleep duration [53]. Nutrition and sleep have a very old relationship. Health is negatively influenced by late-night eating patterns. Dietary intake plays a significant role in sleep quality and sleep wellness. Indeed, some of the nutritional components have proven to be effective during experiments. Nutrition can easily affect hormones and inflammatory markers that can eventually lead to disruption in normal sleep rhythm. Major nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and vitamins play a major role in sleep and sleep disorders.
Researchers concluded that consuming a high carbohydrate diet that is high glycemic index (GI) meals 4 hours before sleep has shortened the sleep onset latency in comparison with individuals who consumed low GI meals. Another study concluded that low GI meals cause difficulty in sleep. It happens due to the alteration in the ratio of tryptophan and other amino acids. In the case of lipids, researchers concluded that intake of foods high in saturated fat during the day caused a shortening in the duration of slow-wave sleep but caused arousal at night. Studies have suggested that a diet that is low in omega-3 disturbs nocturnal sleep by affecting melatonin rhythm and functions of the circadian clock. On the other hand, a report suggested that the intake of fish supplements causes a disturbance in sleep [54]. Insufficient consumption of protein can affect sleep quality and too much protein consumption can lead to difficulty in sleep maintenance [55]. Short sleep influences BMI. Therefore, it is mandatory to maintain a regular sleep cycle [56]. Short sleep duration and poor sleep quality are linked to obesity. One reason is poor diet quality. Diet quality indices are lower in people who sleep <6 hours per day in comparison with the ones who sleep for a long time. Moreover, women are more prone to obesity due to poor sleep quality. It can be explained by differences in leptin and other hormone metabolites that vary in genders and are involved in the sleep-wake cycle along with food intake behavior [57].
Disturbed sleeping patterns can cause irregular eating patterns which include snacks despite the intake of regular meals. Also, the snacking pattern is usually on foods that are high in carbohydrates and fats. This pattern dysregulates the neuroendocrine appetite control system [58]. Sleep quality influences mental health. Not only people can process thoughts better but this allows them to focus on their other activities; such as improvement in academic performance [59]. Sleep quality is drastically affected by snacking patterns at night. A study showed that sleep was reduced by 122 minutes every night with a total bedtime of 5.5 hours. Snacking negatively influenced sleep. An increase in snacking behavior led to sleep restriction. The food consumed was high in carbohydrates and was in the period of 19:00 h to 07:00 h. This pattern allows individuals to consume a major portion of their energy from snacks rather than meals [60]. A randomized control trial on women was done who were regular breakfast eaters. They were made to skip breakfast to study its effects. Breakfast skipping in regular eaters showed high insulin levels and free fatty acids. Also, they had higher pre-lunch hunger and low prelunch satiety [61]. This showed that disturbances in sleep habits and meal consumption were not only prevalent but also it was unsafe for individuals.
A sleep of 7–8 hours is recommended for everyone and a sleep <7 hours can be detrimental to health. A study was conducted to find an association between sleep duration and metabolic syndrome. The researchers concluded that shorter sleep duration is associated with a higher risk of metabolic syndrome and women are prone to this risk more than men [62]. For long sleep duration, many hours have been provided by researchers. They are said to sleep more than 8, 9, and 10 hours is considered to be longer sleep. Furthermore, studies have shown that insufficient sleep duration is not only related to high-calorie intake but also causes changes in hunger. It can result in changes in insulin sensitivity. Ghrelin and leptin are affected. Leptin levels decrease and ghrelin levels rise. Therefore, satiety is reduced and hunger is increased [60].
Poor health is associated with food consumption at night times since the physiological response to eating is altered. A study on healthy individuals by disrupting their circadian rhythm reported that there was a significant decrease in ghrelin and leptin hormones. It not only changed their hunger and appetite but it could contribute to adverse health patterns [63]. A study conducted on adolescents reported that they were more likely to sleep >8 hours on weekends. Also, they slept around 8, 6–8, and <6 hours on weekdays. A fewer sleep than 6 hous could be due to excessive technology use or involvement in activities that could divert their attention from having a healthy sleep [64].
Poor sleep quality plays a major role in the breakfast-skipping pattern. The research was conducted to see the association between breakfast skipping and mood due to poor sleep. They concluded that males who skipped breakfast had fewer mood swings as compared to females. Females who did not have breakfast had anxiety issues. Also, males who used to stay awake for a long time had higher score of depression along with breakfast skipping while females faced fatigue. Breakfast skipping and poor sleep affected mood [65]. Therefore, food and food components affect mood [66]. A study in Brazil on undergraduate students concluded that evening chorotypes were breakfast skippers. On the other hand, morning chrono-type students usually had breakfast and lunch earlier than evening chrono-types. They had high intake of food that was calorie dense including carbohydrates and fats. The individuals were at risk of being overweight [67].
Research on adolescents to check delayed sleep-onset and awakening in the morning. They reported that students with delayed sleep-wake phase disorder had their breakfast on the weekdays and weekends a bit late [68]. Data from healthy adults (n=953) was analyzed to see the association between sleep timings, diet consumption, and post-prandial glycemic control. Poor sleep and bedtime eating routine had more effects on post-glycemic responses to breakfast the next morning. An individual’s sleep pattern was negatively linked to post-prandial glycemic control [69]. Furthermore, another study on how breakfast eating and skipping affect the human body was done. They concluded that regular breakfast eating has positive effects on overall health. It supports adequate nutrient intake which helps in preventing obesity and metabolic disorders [70]. A retrospective cohort study suggested that there is no strong relation between breakfast skipping and weight gain [71]. However, another study suggests that there is a relationship between breakfast skipping and weight gain [72,73]. A meta-analysis and systematic review concluded that there is minimal relation between weight gain and breakfast skipping [74].
Chrononutrition influences individuals in every way. If the individuals are students; their academic performance will be the second thing to be affected after their health. Circadian rhythms negative effects [75]. Figure 2 shows the relationship between less sleep time and high caloric intake along with it which results in body weight gain. In this way, they affect the academic performances of students. Individuals with healthy routines find it easy to go to colleges and universities. Chronotypes influence meal consumption and the timing of food intake. A systematic review of studies from 2000 to 2019 concluded that poor sleep quality and quantity can negatively affect the academic performance of university students [76]. In a cross-sectional study of Japan, they found that students who had intermediate and evening chronotypes had bad mental health and the quality of academic performance was lower as compared to the ones who had morning chronotypes. Evening chronotype students tend to get tired and skip classes more than morning types [16,77]. Another study examining nursing students revealed that 30.4% of them exhibited poor sleeping habits, which consequently resulted in lower academic performance. This evidence suggests that students who work at night and eat along with it are lacking in their academic performance. The quality of education and ability to understand in universities will be altered therefore taking a toll on mental health if the students would not be able to perform well as they wanted to. Although people with evening chronotype tend to have higher weight, currently, there is no supporting literature that would directly link weight gain to poor academic performance in young adults. Another study supported that physical activity with proper nutrition helps students remain focused on their academics. Not only this, they score better and perform well in their classes and exams [78].
The mediterranean diet (MD) is currently the best nutritional intervention for nearly every disease. It limits carbs and focuses more on vegetables and fats in the form of monounsaturated fatty acids. Students of universities who are taking MD are more physically fit, perform well in university, and have better mental health. However, these were observed in students who are not away from home. Therefore, they have everything they need within their range. Students with MD had low stress scores [79]. A study on Australian university students proved a smaller association between a healthy diet with improved CGPA. In China, a study was meant to check an association between sleep disturbances and academic performance in adolescents. Sleep disturbances caused them emotional problems which significantly interacted with academic performances negatively. Also, students with high academic performance had high sleep disturbances [80]. The better the diet, the better performance in universities [81]. This can be used as a base to further investigate if academic performances are influenced by a healthy diet and timing of meal consumption.
A study was conducted on adolescents to check the relationship between weight status and academic performance. Students who were overweight and obese had lower academic performance than the ones who had normal weight ranges [82]. Therefore, it is mandatory to keep weight in normal ranges for better academic performance and school experience. Adequate sleep is necessary and is an important factor for better functioning. Academic performances are highly influenced by sleep quality and quantity. A study in Saudia Arabia was done on university students to see the association between sleep quality mental health and academic performance. They concluded about 62.3% of students had poor sleep and were mostly inactive. Surprisingly, poor sleepers had higher academic performance scores. And the quality of sleep was directly associated with anxiety and depression [83]. A study was done to see the difference in the health and academic performance of day scholars and hostelites. The results showed that 36.5% of hostelites had good health conditions and poor academic performance and 63.5% had good health conditions and good academic performance. Among day scholars, 56.4% had good health while 43.5% had poor health. They concluded that the health status of day scholars was better than hostelites. However, hostelites had a better academic performance as compared to day scholars [84].
A study done in Lahore on female hostelite students to assess their nutritional health reported that many students were overweight and slightly lower numbers of obese females. Many females consumed >5 fast foods per week. They had a low intake of vegetables and fruits. Also, they had a sedentary lifestyle. In conclusion, they said that fast food consumption was prevalent in hostelites [85]. Another study in Lahore was done to assess the relationship between dietary habits and psychological outcomes in day scholars and hostelites. They concluded that normal BMI was common in hostelites. Moreover, they had more stress and poor eating habits along with worsened sleep quality. This study highlighted the fact that students who live in hostels are nutritionally weak and psychological discomfort is more which can result in poor academic performance [86]. Another study on college students suggested that students with insufficient sleep face poor academic performance. But they can be treated by providing lightbased therapy which means avoiding the use of technology before bedtime [87]. Students who have evening chronotype have shown poor academic performance in both schools and universities. Also, if lifestyle changes are not made at the school level, the prevalence is higher in the students when they reach the university stage [88].
Food consumption outside homes is a very common practice among young adults. Individuals like hostelites are included in this category too. Young adults have hectic routines and disturbed eating patterns along with it. A cross-sectional study in Saudia Arabia was done on clinical phase medical students. Students were diagnosed with nomophobia, morning sleepiness, and breakfast skipping, and having dinner at later hours was common for them. Out of 111 students, 44.1% were skipping dinner and 64.8% had late dinners [89]. Previous studies have observed that men are more obese and at risk of metabolic disorders since they have an unhealthy way of living. They prefer foods high in calories and provide quick energy. Moreover, their hormones put them at risk of diseases like DMT2 and CVD. A study in Tanzania was conducted to see how much food consumption is done outside the home. As a result, the prevalence of food consumed outside the homes was 37% by men and 7% by women. In urban areas, this percentage was 77%–81% as compared with the individuals who were from lower backgrounds. Men reported having 2 out of 3 meals outside the home and most of them were ultra-processed foods including rice and fries [90]. Most of the students of universities live in hostels.
A study in Korea concluded that men with disturbed sleeping patterns and factors that overall disturbed their circadian rhythm had higher abdominal obesity [91]. Therefore, their eating pattern is highly affected. Most of them choose foods that are generally not consumed daily but since they are out of options and with limited financial resources, they look for meals providing energy rather than nutrition. A systematic review of published literature from 2009 to 2020 was gathered to see the relationship between eating outside meals with overweight and in adults (>18 years old). Most of the people consuming meals outside the home were males with high incomes yet unmarried. Not only they were having habitual outside food but also had poor diet quality. Their diets were high in carbohydrates, fats, and sodium. They consumed a lesser number of fruits and vegetables. Sugar beverages were very popular among them [92]. Another published literature in the UK suggested that many adults and children consumed meals outside of their homes. They were consuming outside meals weekly which was negatively affecting their health [93].
Circadian rhythm influences individuals’ daily routines. Disturbances in sleep and meal patterns will disrupt the body’s physiology and hormones. These will further increase the risk of diseases. Therefore, it is beneficial to eat according to the biological clock. Moreover, the TRF approach is being used for achieving optimal health. Irregularities in meal patterns and insufficient sleep will affect body weight and BMI. Hence, the academic performance of students will be influenced. People who consume meals outside their homes are observed to be very irregular in terms of sleep week and meal consumption. Also, snacking behavior is common in people who skip breakfast habitually.
In conclusion, eating with a biological clock can help individuals reverse or recover from a disease and create a positive impact on academic performance.
NOTES
Conflicts of Interest
Availability of Data and Material
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Khadija Sajid, Mahnoor Tariq, Rida Zainab. Data Curation: Marriyam Saif, Anam Aslam. Methadology: Marriyam Saif. Supervision: Afifa Tanweer. Validation: Marriyam Saif. Visualization: Marriyam Saif, Anam Aslam, Rida Zainab. Writing—original draft: Marriyam Saif, Anam Aslam. Writing—review & editing: Marriyam Saif, Anam Aslam, Afifa Tanweer.
Acknowledgments
It is with the blessings of Allah Almighty that we were able to start and complete this research. We express our special gratitude to our supervisor and mentor without whom the research would not be possible. She gave her time to read our research and help us where needed. Secondly, we want to give our thanks to our parents and friends have given constant emotional support in this time. Lastly, we want to thank ourselves to complete the research timely.
Figure 1.
Meal skipping and intake according to the clock and its effects (positive and negative). Adapted from Lopez-Minguez et al. Nutrients 2019;11:2624, under the terms of Creative Commons License (CC-BY) [39].
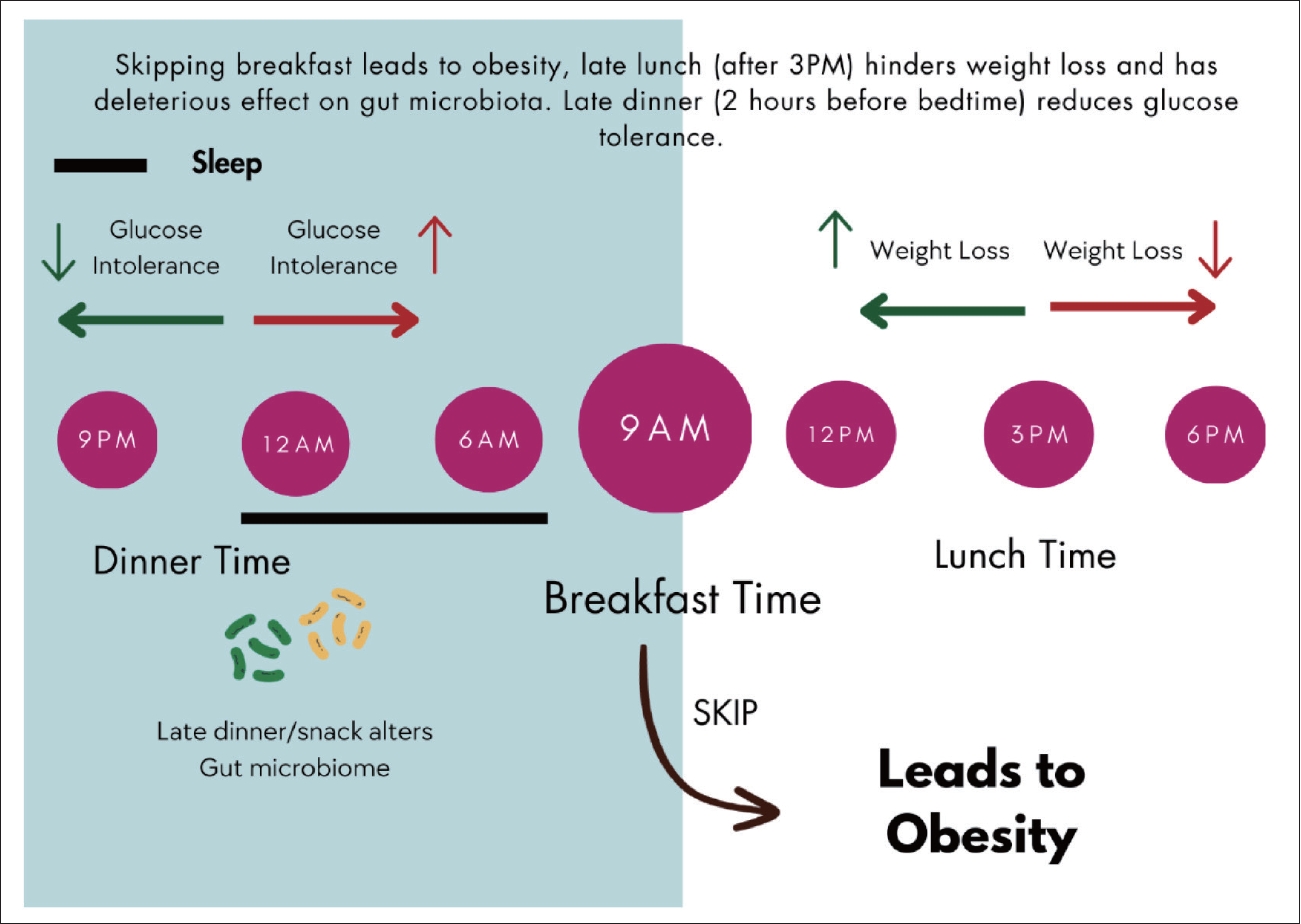
Figure 2.
Less sleep time and high-calorie intake and its influence on body weight. Adapted from Sejbuk et al. Nutrients 2022;14:1912, under the terms of Creative Commons License (CC-BY) [55].
REFERENCES
1. Flanagan A, Bechtold DA, Pot GK, Johnston JD. Chrono‐nutrition: from molecular and neuronal mechanisms to human epidemiology and timed feeding patterns. J Neurochem 2021;157:53–72.



2. Jagannath A, Taylor L, Wakaf Z, Vasudevan SR, Foster RG. The genetics of circadian rhythms, sleep and health. Hum Mol Genet 2017;26(R2): R128–R138.



3. Franzago M, Alessandrelli E, Notarangelo S, Stuppia L, Vitacolonna E. Chrono-nutrition: circadian rhythm and personalized nutrition. Int J Mol Sci 2023;24:2571.



4. Marangoni F, Martini D, Scaglioni S, Sculati M, Donini LM, Leonardi F, et al. Snacking in nutrition and health. Int J Food Sci Nutr 2019;70:909–923.


5. Huang RC. Molecular mechanisms in the circadian rhythm. eLS 2020;Aug 29 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470015902.a0028836.

6. Asher G, Sassone-Corsi P. Time for food: the intimate interplay between nutrition, metabolism, and the circadian clock. Cell 2015;161:84–92.


7. Walker WH 2nd, Walton JC, DeVries AC, Nelson RJ. Circadian rhythm disruption and mental health. Transl Psychiatry 2020;10:28.


8. Almoosawi S, Vingeliene S, Karagounis LG, Pot GK. Chrono-nutrition: a review of current evidence from observational studies on global trends in time-of-day of energy intake and its association with obesity. Proc Nutr Soc 2016;75:487–500.


10. Bailey SM, Udoh US, Young ME. Circadian regulation of metabolism. J Endocrinol 2014;222:R75–R96.



12. Castro MA, Garcez MR, Pereira JL, Fisberg RM. Eating behaviours and dietary intake associations with self-reported sleep duration of free-living Brazilian adults. Appetite 2019;137:207–217.


13. Serin Y, Acar Tek N. Effect of circadian rhythm on metabolic processes and the regulation of energy balance. Ann Nutr Metab 2019;74:322–330.



14. Roßbach S, Diederichs T, Nöthlings U, Buyken AE, Alexy U. Relevance of chronotype for eating patterns in adolescents. Chronobiol Int 2018;35:336–347.


15. Maukonen M, Kanerva N, Partonen T, Kronholm E, Tapanainen H, Kontto J, et al. Chronotype differences in timing of energy and macronutrient intakes: a population-based study in adults. Obesity 2017;25:608–615.



16. Kayaba M, Matsushita T, Katayama N, Inoue Y, Sasai-Sakuma T. Sleepwake rhythm and its association with lifestyle, health-related quality of life and academic performance among Japanese nursing students: a cross-sectional study. BMC Nurs 2021;20:225.




17. Papakonstantinou E, Oikonomou C, Nychas G, Dimitriadis GD. Effects of diet, lifestyle, chrononutrition and alternative dietary interventions on postprandial glycemia and insulin resistance. Nutrients 2022;14:823.



18. Mazri FH, Manaf ZA, Shahar S, Mat Ludin AF, Abdul Basir SM. Development and evaluation of integrated chrono-nutrition weight reduction program among overweight/obese with morning and evening chronotypes. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022;19:4469.



19. Acosta-Rodríguez VA, Rijo-Ferreira F, Green CB, Takahashi JS. Importance of circadian timing for aging and longevity. Nat Commun 2021;12:2862.


20. Froy O. Circadian rhythms, nutrition and implications for longevity in urban environments. Proc Nutr Soc 2018;77:216–222.


21. Manoogian ENC, Panda S. Circadian rhythms, time-restricted feeding, and healthy aging. Ageing Res Rev 2017;39:59–67.



22. Vernia F, Di Ruscio M, Ciccone A, Viscido A, Frieri G, Stefanelli G, et al. Sleep disorders related to nutrition and digestive diseases: a neglected clinical condition. Int J Med Sci 2021;18:593–603.



23. Wehrens SMT, Christou S, Isherwood C, Middleton B, Gibbs MA, Archer SN, et al. Meal timing regulates the human circadian system. Curr Biol 2017;27:1768–1775.



24. Scoditti E, Garbarino S. Nutrition, sleep, circadian rhythms, and health implications: “Come Together”. Nutrients 2022;14:5105.



25. Veronda AC, Allison KC, Crosby RD, Irish LA. Development, validation and reliability of the Chrononutrition Profile - Questionnaire. Chronobiol Int 2020;37:375–394.



26. Meyer N, Harvey AG, Lockley SW, Dijk DJ. Circadian rhythms and disorders of the timing of sleep. Lancet 2022;400:1061–1078.


27. Gupta NJ. Lifestyle and circadian health: where the challenges lie? Nutr Metab Insights 2019;12:1178638819869024.




28. Parameswaran G, Ray DW. Sleep, circadian rhythms, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2022;96:12–20.




29. Wharton S, Lau DCW, Vallis M, Sharma AM, Biertho L, Campbell-Scherer D, et al. Obesity in adults: a clinical practice guideline. CMAJ 2020;192:E875–E891.



30. Garcia-Rios A, Ordovas JM. Chronodisruption and cardiovascular disease. Clin Investig Arterioscler 2022;34 Suppl 1:S32–S37.


31. Hawley JA, Sassone-Corsi P, Zierath JR. Chrono-nutrition for the prevention and treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes: from mice to men. Diabetologia 2020;63:2253–2259.



32. Gupta CC, Vincent GE, Coates AM, Khalesi S, Irwin C, Dorrian J, et al. A time to rest, a time to dine: sleep, time-restricted eating, and cardiometabolic health. Nutrients 2022;14:420.



33. Zeb F, Wu X, Fatima S, Zaman MH, Khan SA, Safdar M, et al. Time-restricted feeding regulates molecular mechanisms with involvement of circadian rhythm to prevent metabolic diseases. Nutrition 2021;89:111244.


34. Tahara Y, Qian J, Oike H, Escobar C. Editorial: the present and future of chrono-nutrition studies. Front Nutr 2023;10:1183320.



35. Adafer R, Messaadi W, Meddahi M, Patey A, Haderbache A, Bayen S, et al. Food timing, circadian rhythm and chrononutrition: a systematic review of time-restricted eating’s effects on human health. Nutrients 2020;12:3770.



36. Boege HL, Bhatti MZ, St-Onge MP. Circadian rhythms and meal timing: impact on energy balance and body weight. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2021;70:1–6.



37. Takahashi M, Tahara Y. Timing of food/nutrient intake and its health benefits. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 2022;68(Supplement): S2–S4.


38. Almoosawi S, Vingeliene S, Gachon F, Voortman T, Palla L, Johnston JD, et al. Chronotype: implications for epidemiologic studies on chrono-nutrition and cardiometabolic health. Adv Nutr 2019;10:30–42.



39. Lopez-Minguez J, Gómez-Abellán P, Garaulet M. Timing of breakfast, lunch, and dinner. Effects on obesity and metabolic risk. Nutrients 2019;11:2624.



40. Rácz B, Dušková M, Stárka L, Hainer V, Kunešová M. Links between the circadian rhythm, obesity and the microbiome. Physiol Res 2018;67(Suppl 3): S409–S420.

41. Kolbe I, Leinweber B, Brandenburger M, Oster H. Circadian clock network desynchrony promotes weight gain and alters glucose homeostasis in mice. Mol Metab 2019;30:140–151.



42. Chaput JP, McHill AW, Cox RC, Broussard JL, Dutil C, da Costa BGG, et al. The role of insufficient sleep and circadian misalignment in obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2023;19:82–97.




43. Ward ZJ, Bleich SN, Cradock AL, Barrett JL, Giles CM, Flax C, et al. Projected U.S. state-level prevalence of adult obesity and severe obesity. N Engl J Med 2019;381:2440–2450.


44. Basolo A, Bechi Genzano S, Piaggi P, Krakoff J, Santini F. Energy balance and control of body weight: possible effects of meal timing and circadian rhythm dysregulation. Nutrients 2021;13:3276.



45. Mazri FH, Manaf ZA, Shahar S, Mat Ludin AF, Karim NA. Improvement in chrono-nutrition is associated with robust weight loss outcomes: an extension of the feasibility study. Chronobiol Int 2023;40:272–283.


46. Pot GK. Sleep and dietary habits in the urban environment: the role of chrono-nutrition. Proc Nutr Soc 2018;77:189–198.


48. Poggiogalle E, Jamshed H, Peterson CM. Circadian regulation of glucose, lipid, and energy metabolism in humans. Metabolism 2018;84:11–27.



49. Alkhulaifi F, Darkoh C. Meal timing, meal frequency and metabolic syndrome. Nutrients 2022;14:1719.



50. Paoli A, Tinsley G, Bianco A, Moro T. The influence of meal frequency and timing on health in humans: the role of fasting. Nutrients 2019;11:719.



51. Mirghani H. The effect of breakfast skipping and late night eating on body mass index and glycemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cureus 2021;13:e15853.



52. Xiao Q, Garaulet M, Scheer FAJL. Meal timing and obesity: interactions with macronutrient intake and chronotype. Int J Obes (Lond) 2019;43:1701–1711.




53. Iao SI, Jansen E, Shedden K, O’Brien LM, Chervin RD, Knutson KL, et al. Associations between bedtime eating or drinking, sleep duration and wake after sleep onset: findings from the American time use survey. Br J Nutr 2022;127:1888–1897.



54. Zhao M, Tuo H, Wang S, Zhao L. The effects of dietary nutrition on sleep and sleep disorders. Mediators Inflamm 2020;2020:3142874.




55. Sejbuk M, Mirończuk-Chodakowska I, Witkowska AM. Sleep quality: a narrative review on nutrition, stimulants, and physical activity as important factors. Nutrients 2022;14:1912.



56. Chang WP, Yang CM. Influence of sleep-wake cycle on body mass index in female shift-working nurses with sleep quality as mediating variable. Ind Health 2020;58:161–169.


57. Hur S, Oh B, Kim H, Kwon O. Associations of diet quality and sleep quality with obesity. Nutrients 2021;13:3181.



58. Papatriantafyllou E, Efthymiou D, Zoumbaneas E, Popescu CA, Vassilopoulou E. Sleep deprivation: effects on weight loss and weight loss maintenance. Nutrients 2022;14:1549.



59. Scott AJ, Webb TL, Martyn-St James M, Rowse G, Weich S. Improving sleep quality leads to better mental health: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Sleep Med Rev 2021;60:101556.



60. Nedeltcheva AV, Kilkus JM, Imperial J, Kasza K, Schoeller DA, Penev PD. Sleep curtailment is accompanied by increased intake of calories from snacks. Am J Clin Nutr 2009;89:126–133.


61. Thomas EA, Higgins J, Bessesen DH, McNair B, Cornier MA. Usual breakfast eating habits affect response to breakfast skipping in overweight women. Obesity 2015;23:750–759.



62. Smiley A, King D, Bidulescu A. The association between sleep duration and metabolic syndrome: the NHANES 2013/2014. Nutrients 2019;11:2582.



63. McHill AW, Hull JT, Klerman EB. Chronic circadian disruption and sleep restriction influence subjective hunger, appetite, and food preference. Nutrients 2022;14:1800.



64. Lima SBDS, Ferreira-Lima W, Lima FÉB, Lima FB, Santos A, Fernandes CAM, et al. Sleep hours: risk behavior in adolescents from different countries. Cien Saude Colet 2020;25:957–965.


65. Chang ZS, Boolani A, Conroy DA, Dunietz T, Jansen EC. Skipping breakfast and mood: the role of sleep. Nutr Health 2021;27:373–379.



66. Garbarino S, Garbarino E, Lanteri P. Cyrcadian rhythm, mood, and temporal patterns of eating chocolate: a scoping review of physiology, findings, and future directions. Nutrients 2022;14:3113.



67. Mirghani HO, Albalawi KS, Alali OY, Albalawi WM, Albalawi KM, Aljohani TR, et al. Breakfast skipping, late dinner intake and chronotype (eveningness-morningness) among medical students in Tabuk City, Saudi Arabia. Pan Afr Med J 2019;34:178.



68. Berendsen M, Boss M, Smits M, Pot GK. Chrono-nutrition and diet quality in adolescents with delayed sleep-wake phase disorder. Nutrients 2020;12:539.



69. Tsereteli N, Vallat R, Fernandez-Tajes J, Delahanty LM, Ordovas JM, Drew DA, et al. Impact of insufficient sleep on dysregulated blood glucose control under standardised meal conditions. Diabetologia 2022;65:356–365.




70. Yoon SR, Choi M, Kim OY. Effect of breakfast consumption and meal time regularity on nutrient intake and cardiometabolic health in Korean adults. J Lipid Atheroscler 2021;10:240–250.




71. Yamamoto R, Tomi R, Shinzawa M, Yoshimura R, Ozaki S, Nakanishi K, et al. Associations of skipping breakfast, lunch, and dinner with weight gain and overweight/obesity in university students: a retrospective cohort study. Nutrients 2021;13:271.



72. Martínez CF, Ortiz-Panozo E, Mattei J, Campos H, Flores-Aldana M, Lajous M. Breakfast frequency is inversely associated with weight gain in a cohort of Mexican women. J Nutr 2021;151:405–411.



73. Ma X, Chen Q, Pu Y, Guo M, Jiang Z, Huang W, et al. Skipping breakfast is associated with overweight and obesity: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Obes Res Clin Pract 2020;14:1–8.


74. Wicherski J, Schlesinger S, Fischer F. Association between breakfast skipping and body weight-a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational longitudinal studies. Nutrients 2021;13:272.



75. Rijo-Ferreira F, Takahashi JS. Genomics of circadian rhythms in health and disease. Genome Med 2019;11:82.




76. Suardiaz-Muro M, Morante-Ruiz M, Ortega-Moreno M, Ruiz MA, Martín-Plasencia P, Vela-Bueno A. [Sleep and academic performance in university students: a systematic review]. Rev Neurol 2020;71:43–53.Spanish.

77. Marta OFD, Kuo SY, Bloomfield J, Lee HC, Ruhyanudin F, Poynor MY, et al. Gender differences in the relationships between sleep disturbances and academic performance among nursing students: a cross-sectional study. Nurse Educ Today 2020;85:104270.


78. Asigbee FM, Whitney SD, Peterson CE. The link between nutrition and physical activity in increasing academic achievement. J Sch Health 2018;88:407–415.



79. Antonopoulou M, Mantzorou M, Serdari A, Bonotis K, Vasios G, Pavlidou E, et al. Evaluating mediterranean diet adherence in university student populations: does this dietary pattern affect students’ academic performance and mental health? Int J Health Plann Manage 2020;35:5–21.



80. Jiang Y, Guo L, Lai W, Li Y, Sun X, Zhao H, et al. Association of emotional and behavioral problems with sleep disturbance among Chinese adolescents: the moderation effect of academic performance. J Affect Disord 2023;330:94–100.


81. Whatnall MC, Patterson AJ, Burrows TL, Hutchesson MJ. Higher diet quality in university students is associated with higher academic achievement: a cross-sectional study. J Hum Nutr Diet 2019;32:321–328.



82. Ma L, Gao L, Chiu DT, Ding Y, Wang Y, Wang W. Overweight and obesity impair academic performance in adolescence: a national cohort study of 10,279 adolescents in China. Obesity 2020;28:1301–1309.



83. Al-Khani AM, Sarhandi MI, Zaghloul MS, Ewid M, Saquib N. A cross-sectional survey on sleep quality, mental health, and academic performance among medical students in Saudi Arabia. BMC Res Notes 2019;12:665.




84. Rasool SG, Amjad F, Zuha A, Ahmad A. Health status and academic progress among day scholars vs hostelites in allied health sciences students: health status and academic progress among day scholars vs hostelites. PBMJ 2022;5:66–69.
85. Shabbir T, Aslam M, Kamran H, Liaqat M, Khan R, Saleem M. Assessment of nutritional status among university hostelite girls in Lahore city. AJAHS 2020;5:40–46.
86. Qureshi A, Aslam M, Kamran H, Sandhu K, Fatima D. Comparison of dietary habits and psychological outcomes in hostelites and day scholars : dietary habits and outcomes in hostelites and day scholars. Diet Factor 2022;3:22–27.
87. Phillips AJK, Clerx WM, O’Brien CS, Sano A, Barger LK, Picard RW, et al. Irregular sleep/wake patterns are associated with poorer academic performance and delayed circadian and sleep/wake timing. Sci Rep 2017;7:3216.




88. Tonetti L, Natale V, Randler C. Association between circadian preference and academic achievement: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Chronobiol Int 2015;32:792–801.


89. Mirghani HO, Alanazi MA. Nomophobia, daytime sleepiness, and chrono nutrition among medical students in Tabuk city, Saudi Arabia. BNIHS 2022;140:1441–1448.
90. Ambikapathi R, Irema I, Lyatuu I, Caswell B, Mosha D, Nyamsangia S, et al. Gender and age differences in meal structures, food away from home, chrono-nutrition, and nutrition intakes among adults and children in Tanzania using a newly developed tablet-based 24-hour recall tool. Curr Dev Nutr 2022;6:nzac015.




91. Kim HJ, Choi S, Kim K, Park H, Kim KH, Park SM. Association between misalignment of circadian rhythm and obesity in Korean men: Sixth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Chronobiol Int 2020;37:272–280.