|
 |
- Search
| Chronobiol Med > Volume 3(1); 2021 > Article |
|
Abstract
Melatonin and serotonin are considered to be the important neurotransmitter and prime hormones responsible for the body homeostasis. The melatonin exert its effect on insulin signaling through melatonin receptors (MT-1 and MT-2). Similarly, 5-hydroxytryptophan, also plays an important role in insulin secretion, ╬▓-cells function thereby contributing an important role in diabetes management. Several animals and clinical studies suggested that supplementation of N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine and 5-hydroxytryptophan improves the insulin release from the ╬▓-cells of the pancreas and can be used as prospective therapy in management of diabetes and its associated complications.
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a global health metabolic disorder that affected 387 million people with a mortality of 3.4 million due to hyperglycemia according to World Health Organization (WHO) [1]. It is predicted that the number of deaths will get double between the year 2000 and 2030 [2]. The number of subjects with diabetes rose from 108 million from 1980 to 422 million in 2014 [3]. WHO in their reported quoted that diabetes among adults over 18 years of age rose from 4.7% in 1980 to 8.5% in 2014 [4]. DM is a chronic metabolic disease that befalls due to failure or insufficiency of the pancreas to make insulin or when the body is not able to sense that insulin. There are two major categories of DM; the first one is type 1 DM also known as insulin-dependent DM or juvenile or childhood-onset diabetes, which is characterized by insufficient insulin production due to pancreas damaged by autoimmune disease. Another type of DM includes type 2 DM (T2DM), which is characterized by abnormally high insulin resistance due to factors associated like age, obesity, sedentary lifestyle and other environmental factors [5,6]. Patients presenting T2DM often accompanied by the microvascular and macrovascular complications like diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic neuropathy, and cardiovascular diseases due to uncontrolled hyperglycemia [6]. Hyperglycemia produces reactive oxygen species (ROS) via mitochondrial dysfunction, glucose auto-oxidation, non-enzymatic glycation of bio-macromolecules of DNA, lipids and proteins [7]. Increase level of intracellular and extracellular glucose initiates generation of free radicals or ROS that in turn leads to the diabetes-associated complications.
The impression of the pineal hormone on insulin secretion, carbohydrate metabolism and blood glucose levels has been demonstrated recently. Melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine) is a tryptophan derived endocrine agent, primarily synthesized by the pineal gland along with several extra pineal sites of the retina, gut and digestive tract [8]. In the previously published study on Goto-Kakizaki rats, low levels of serum melatonin was reported in DM in spite of high levels of insulin [9]. This hormone is associated with DM pathways in various ways. Recent evidence showed that melatonin reduces the complications associated with DM and ameliorate the oxidative damage [10]. This hormone also believed to perform an antioxidant role in ╬▓-cells by scavenging the ROS, this in turn reduces the micro- and macrovascular complications [11].
In the pancreatic islet cells, another hormone named as serotonin also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) plays an important role in pancreatic health via autocrine signalling, generating an increase in ╬▓-cell mass during metabolic changes of diabetes and its associated complications. 5-HT is a neurotransmitter that is originated from the tryptophan amino acid following chemistry between tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) and aromatic acid decarboxylase. The 5-HT binds to its corresponding receptor 5-HTR and exert biological functions [12,13]. There are two forms of TPH discovered until date: one is TPH1, which is expressed or present in peripheral non-neuronal tissues, and another one is TPH2, present in the neurons of the central and enteric nervous systems [12,13]. In the study published, it was found that TPH1 expression and 5-HT generation synergistically increased in pancreatic ╬▓-cells and it was also reported that during the pregnancy, 5-HT released from ╬▓-cells in the local microenvironment and exert increased ╬▓-cell proliferation and insulin secretion mediated by HTR2B and HTR3, respectively [14,15]. It has been found that the 5-HT generation in ╬▓-cells increases during the perinatal period [14,15].
In present work, we focused on the prospective role of 5-HT and melatonin (MT) in the maintenance of ╬▓-cell health and increased insulin secretion. Furthermore, these hormones may be used as an important tool in the management of diabetes and its associated micro- and macrovascular complications.
A pancreatic ╬▓-cell failure is a key event in the development of T2DM that is characterized by the loss of the ╬▓-cell mass and their dysfunction [16,17]. It is still complex to resolve the tale associated with the pathophysiology of the ╬▓-cell dysfunction in T2DM, but it is attributed by the loss of the glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) along with loss of ╬▓-cell in T2DM due to increased ╬▓-cell apoptosis [17-19]. It is reported recently through genomewide analysis study (GWAS) that variation in melatonin receptor 2 (MT-2) is associated with the development of the ╬▓-cell failure and initiation of the pathogenesis of T2DM [20]. This pathophysiology can also be explained as MT-2 variant showed significant inhibition on GSIS. It is still a matter of debate that genetic linkage between ╬▓-cell and MT-2 receptor signalling plays an important role in the regulation and control of ╬▓-cell function and insulin release in T2DM.
It has been reported in previously published studies that impairment in MT production or secretion is associated with DM [21,22]. Endocrine cells of the pineal gland secret and produce MT hormone following nocturnal secretion pattern and production. It has been seen that T2DM patients have significantly reduced nocturnal MT secretion and production [21]. In one of the studies conducted in animals with T2DM, it has been found that there is impaired nocturnal MT secretion upon induction of hyperglycemia [23]. The significant reduction in nocturnal MT secretion in T2DM subjects is attributed due to the decrease in size of pineal gland along with its loss and up-regulation of inhibitory ╬▒-adrenoreceptors [23]. It is recently reported that significant loss of nocturnal MT is associated with a higher risk of developing T2DM [22].
Recently, it has been reported that ╬▓-cell functioning is associated with the diurnal activation of MT receptors and circadian rhythms [24]. MT signalling is also responsible for the metabolic control of organism that is mediated by two high-affinity Gi/o receptors (MT-1 and MT-2) along with activation of Gi-coupled receptor activation [25]. In one of the study, it was shown that acute exposure of MT, inhibits adenylate cyclase (AC) activity and along with this it also attenuates cAMP production that significantly reduces the protein kinase A (PKA) and cAMP-responsive elementbinding protein (CREB) [25]. In another study, it was found that activation of MT receptor leads to the activation of the cAMPPKA-CREB cascade in the ╬▓-cells [26]. Oxidative stress also plays an important role in diabetes and the onset of its associated complications and is effectively attenuate the anti-oxidative effect of the MT. In one of the previously published study, it was found that MT showed a protective role for the ╬▓-cells of the pancreas against oxidative stress [27]. In another clinical study, MT supplement showed good glycemic control mediated by improved insulin sensitivity and lower fasting blood glucose level [28].
MT secretion pathway is controlled by biological circadian rhythm, where MT production is released both in day and night time and inhibit in presence of the sunlight. The main role of the MT in the human body is to regulate night and day cycles or in another words we can say that MT is responsible for sleep and awake process. As it is evident that darkness promotes the MT secretion and transmit the signal of sleep. Moreover, the presence of the light reduces the concentration of the MT secretion that signals awake cycle in daytime.
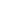
MT synthesis involves a series of reaction, in which tryptophan amino acid converted into serotonin, which further acetylates by the enzyme serotonin-N-acetyltransferase (SNAT) and finally converted into MT by hydroxy indole-O-methyltransferase (HIOMT). In humans, two types of MT receptors are foundŌĆöone is MT-1 and second is MT-2. The MT receptors are G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) [22,29]. Insulin secretion is believed to mediate by both MT1 and MT2 receptors. The MT receptors bind to inhibitory G-proteins (Gi) that subsequently inhibits the AC/cAMP and GC/cGMP pathway that significantly reduces the levels of cAMP. The cAMP is an activator for insulin secretion through ╬▓-cells of the pancreas. During diurnal environment it has been found that there are low levels of MT, while insulin level is found to be elevated, while in the nocturnal environment, MT level is raised significantly, thereby decreasing the insulin level leading to hyperglycemia [30]. Figure 1 showing the protective role of MT under hyperglycemia environment in Schwann cells.
5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HT) is believed to be present in the vesicles, in which insulin is present. It has been known that 5-HT is associated with the regulation and control of blood glucose levels especially in DM [31,32]. It has been reported recently that 5-HT is involved in the regulation of ╬▓-cells to pregnancy [33]. It has been found that in pregnancy secretion of lactogen significantly increases the expression of Tph1 in pancreatic ╬▓-cells that in turn results in a massive generation of 5-HT in ╬▓-cells [33]. Islet 5-HT acts both as an autocrine and paracrine signalling manner mediated by a 5-HT3 receptor that increases the glucose responsiveness of ╬▓-cells that results in increased overall islet GSIS [34]. In a recently published study, it was demonstrated that 5-HT controls or regulates insulin secretion [34].
Serotonin (5-HT) plays a role in neuronal and non-neuronal systems. It acts both as a hormone and as a neurotransmitter. 5-HT acts as a neurotransmitter and can be associated with alteration in mood, behaviour, sleep cycles and appetite [35]. In a recent study, it was found that serotonin present in the pancreatic cell-bound directly to GTPase enzymes thereby blocking transglutaminase and reducing insulin secretion [36]. Pancreatic ╬▓-cells produce and store 5-HT which later coreleased with insulin as quoted in the previously published study [37]. In one of the recently published study, it was reported that basal 5-HT levels in pancreatic ╬▓-cells play an important role in GSIS mediated through the 5-HT3 receptor (Htr3) [38].
MT and serotonin both can be used as protective agent in hyperglycemia induced damage and management of the DM. In DM, it is well evident that there is deficient of insulin from the ╬▓-cells. These hormones (MT and serotonin) can be loaded into the specialized nanoparticles loading system that can be further given to the pancreatic ╬▓-cells for the maintenance of their health and enhancing insulin production. These hormones in future can also given as therapy in management of DM with nanostructured lipid vesicles, extracellular vesicles, and carbon nanotubes for their efficient absorption inside the pancreatic ╬▓-cells.
MT is a nocturnal hormone that is synthesized by diverse cell types and has an exceptional ability to cross the membrane. MT and serotonin have been associated with insulin secretion and release and have a prime role in the management of diabetes and its associated complications. The significant irregularity in the glycemic control and rise in fasting blood glucose level are associated with T2DM that results from the destruction of pancreatic ╬▓-cells and loss of ╬▓-cell function that in turn result in a deficiency of insulin release. Several animals and clinical studies suggested that supplementation of MT and serotonin can be used as prospective therapy in the management of DM and improvement of insulin specificity and sensitivity.
NOTES
Conflicts of Interest
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Alok Raghav, Brijesh Kumar Mishra, Renu Tomar, Supriya Raghav. Data curation: Alok Raghav, Brijesh Kumar Mishra, Renu Tomar, Supriya Raghav. Formal analysis: Alok Raghav, Brijesh Kumar Mishra, Renu Tomar, Supriya Raghav. Investigation: Alok Raghav, Brijesh Kumar Mishra. Methodology: Alok Raghav. Project administration: Alok Raghav. Resources: Alok Raghav. Software: Renu Tomar, Supriya Raghav. Supervision: Alok Raghav. Validation: Alok Raghav, Goo-Bo Jeong. Visualization: Alok Raghav. WritingŌĆöoriginal draft: Renu Tomar, Supriya Raghav. WritingŌĆöreview & editing: Alok Raghav, Goo-Bo Jeong, Brijesh Kumar Mishra.
Figure┬Ā1.
Mechanism showing the action of melatonin in hyperglycemia induced apoptosis in nerve Schwann cells. MTORC1: mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1, MTORC2: mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2, Mcl1: myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein. Adpated from Tiong et al. Antioxidants (Basel) 2019;8:198, under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license [39].
REFERENCES
1. You WP, Henneberg M. Type 1 diabetes prevalence increasing globally and regionally: the role of natural selection and life expectancy at birth. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care 2016;4:e000161.



2. Hossain P, Kawar B, El Nahas M. Obesity and diabetes in the developing world--a growing challenge. N Engl J Med 2007;356:213ŌĆō215.


3. World Health Organization. Diabetes. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes. Accessed January 31, 2021.
4. Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration; Sarwar N, Gao P, Seshasai SR, Gobin R, Kaptoge S, et al. Diabetes mellitus, fasting blood glucose concentration, and risk of vascular disease: a collaborative meta-analysis of 102 prospective studies. Lancet 2010;375:2215ŌĆō2222.



5. Prasad RB, Groop L. Genetics of type 2 diabetes-pitfalls and possibilities. Genes (Basel) 2015;6:87ŌĆō123.



6. Wu Y, Ding Y, Tanaka Y, Zhang W. Risk factors contributing to type 2 diabetes and recent advances in the treatment and prevention. Int J Med Sci 2014;11:1185ŌĆō1200.



7. Bondeva T, Wolf G. Reactive oxygen species in diabetic nephropathy: friend or foe? Nephrol Dial Transplant 2014;29:1998ŌĆō2003.


8. Szewczyk PB, Dziuba AM, Poniewierka E. MelatoninŌĆōmetabolism and the role of pineal hormone. Nurs Public Health 2018;8:135ŌĆō139.

9. Frese T, Bach AG, M├╝hlbauer E, P├Čnicke K, Br├Čmme HJ, Welp A, et al. Pineal melatonin synthesis is decreased in type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. Life Sci 2009;85:526ŌĆō533.


10. Reiter RJ, Mayo JC, Tan DX, Sainz RM, Alatorre-Jimenez M, Qin L. Melatonin as an antioxidant: under promises but over delivers. J Pineal Res 2016;61:253ŌĆō278.


11. Wang J, Wang H. Oxidative stress in pancreatic beta cell regeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017;2017:1930261.



12. Walther DJ, Peter JU, Bashammakh S, H├Črtnagl H, Voits M, Fink H, et al. Synthesis of serotonin by a second tryptophan hydroxylase isoform. Science 2003;299:76.


13. Zhang X, Beaulieu JM, Sotnikova TD, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG. Tryptophan hydroxylase-2 controls brain serotonin synthesis. Science 2004;305:217.


14. Kim H, Toyofuku Y, Lynn FC, Chak E, Uchida T, Mizukami H, et al. Serotonin regulates pancreatic beta cell mass during pregnancy. Nat Med 2010;16:804ŌĆō808.



15. Ohara-Imaizumi M, Kim H, Yoshida M, Fujiwara T, Aoyagi K, Toyofuku Y, et al. Serotonin regulates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from pancreatic ╬▓ cells during pregnancy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013;110:19420ŌĆō19425.



16. Brunzell JD, Robertson RP, Lerner RL, Hazzard WR, Ensinck JW, Bierman EL, et al. Relationships between fasting plasma glucose levels and insulin secretion during intravenous glucose tolerance tests. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1976;42:222ŌĆō229.


17. Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel R, Rizza RA, Butler PC. ╬▓-Cell deficit and increased ╬▓-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2003;52:102ŌĆō110.


18. Marchetti P, Del Guerra S, Marselli L, Lupi R, Masini M, Pollera M, et al. Pancreatic islets from type 2 diabetic patients have functional defects and increased apoptosis that are ameliorated by metformin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004;89:5535ŌĆō5541.


19. Yoneda S, Uno S, Iwahashi H, Fujita Y, Yoshikawa A, Kozawa J, et al. Predominance of ╬▓-cell neogenesis rather than replication in humans with an impaired glucose tolerance and newly diagnosed diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2013;98:2053ŌĆō2061.


20. Lyssenko V, Nagorny CL, Erdos MR, Wierup N, Jonsson A, Sp├®gel P, et al. Common variant in MTNR1B associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes and impaired early insulin secretion. Nat Genet 2009;41:82ŌĆō88.


21. M├żntele S, Otway DT, Middleton B, Bretschneider S, Wright J, Robertson MD, et al. Daily rhythms of plasma melatonin, but not plasma leptin or leptin mRNA, vary between lean, obese and type 2 diabetic men. PLoS One 2012;7:e37123.



22. McMullan CJ, Schernhammer ES, Rimm EB, Hu FB, Forman JP. Melatonin secretion and the incidence of type 2 diabetes. JAMA 2013;309:1388ŌĆō1396.



23. Bach AG, M├╝hlbauer E, Peschke E. Adrenoceptor expression and diurnal rhythms of melatonin and its precursors in the pineal gland of type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. Endocrinology 2010;151:2483ŌĆō2493.


24. Nishiyama K, Hirai K. The melatonin agonist ramelteon induces duration-dependent clock gene expression through cAMP signaling in pancreatic INS-1 ╬▓-cells. PLoS One 2014;9:e102073.



25. von Gall C, Stehle JH, Weaver DR. Mammalian melatonin receptors: molecular biology and signal transduction. Cell Tissue Res 2002;309:151ŌĆō162.


26. Kemp DM, Ubeda M, Habener JF. Identification and functional characterization of melatonin Mel 1a receptors in pancreatic ╬▓ cells: potential role in incretin-mediated cell function by sensitization of cAMP signaling. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2002;191:157ŌĆō166.


27. Ergenc M, Ozacmak HS, Turan I, Ozacmak VH. Melatonin reverses depressive and anxiety like-behaviours induced by diabetes: involvement of oxidative stress, age, rage and S100B levels in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of rats. Arch Physiol Biochem 2019;Nov 15 [Epub]. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1080/13813455.2019.1684954.

28. Doosti-Irani A, Ostadmohammadi V, Mirhosseini N, Mansournia MA, Reiter RJ, Kashanian M, et al. Correction: the effects of melatonin supplementation on glycemic control: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Horm Metab Res 2018;50:e6.


29. Devavry S, Legros C, Brasseur C, Cohen W, Guenin SP, Delagrange P, et al. Molecular pharmacology of the mouse melatonin receptors MT1 and MT2. Eur J Pharmacol 2012;677:15ŌĆō21.


30. la Fleur SE, Kalsbeek A, Wortel J, Van Der Vliet J, Buijs RM. Role for the pineal and melatonin in glucose homeostasis: pinealectomy increases night-time glucose concentrations. J Neuroendocrinol 2001;13:1025ŌĆō1032.


31. Gershon MD, Ross LL. Location of sites of 5-hydroxytryptamine storage and metabolism by radioautography. J Physiol 1966;186:477ŌĆō492.



32. Ekholm R, Ericson LE, Lundquist I. Monoamines in the pancreatic islets of the mouse. Subcellular localization of 5-hydroxytryptamine by electron microscopic autoradiography. Diabetologia 1971;7:339ŌĆō348.



33. Ernst S, Demirci C, Valle S, Velazquez-Garcia S, Garcia-Oca├▒a A. Mechanisms in the adaptation of maternal ╬▓-cells during pregnancy. Diabetes Manag (Lond) 2011;1:239ŌĆō248.



34. Kim K, Oh CM, Ohara-Imaizumi M, Park S, Namkung J, Yadav VK, et al. Functional role of serotonin in insulin secretion in a diet-induced insulinresistant state. Endocrinology 2015;156:444ŌĆō452.


35. Zucker MB. A study of the substances in blood serum and platelets which stimulate smooth muscle. Am J Physiol 1944;142:12ŌĆō26.

37. Jaim-Etcheverry G, Zieher LM. Electron microscopic cytochemistry of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) in the beta cells of guinea pig endocrine pancreas. Endocrinology 1968;83:917ŌĆō923.